Table Of Contents
-
Key Highlights
-
Understanding Zero Carb vs. Low Carb: The Critical Difference
-
Zero Carb Animal-Based Foods: The Foundation
-
Zero Carb Dairy & Eggs: What's Truly Carb-Free?
-
The Best Zero Carb Processed Meats and Snacks
-
Zero Carb Fats and Oils: Pure Energy Sources
-
Virtually Zero Carb Vegetables and Herbs
-
Zero Carb Drinks and Beverages
-
Zero Carb Condiments and Seasonings
- Zero Carb Meal Planning & Sample Days
- Zero Carb Cooking Methods & Techniques
-
Blood Sugar Impact Analysis
-
Interactive Zero Carb Food Tools
-
Advanced Zero Carb Diagrams
Key Highlights
- True zero carb foods are exclusively animal-based: meats, fish, shellfish, and pure animal fats contain absolutely no carbohydrates
- Most plant foods contain trace carbs, but certain leafy greens and herbs qualify as “virtually zero” with less than 1g per serving
- Dairy and eggs are nearly zero carb, though most cheeses contain up to 1g per ounce—always verify nutrition labels
- Processed foods hide unexpected sugars and starches—stick to certified “carb-free” labeled items when possible
- Beverages like water, plain tea, coffee, and distilled spirits are safe choices for zero carb diets
- Hidden carbs are the number one pitfall for those following strict zero-carb eating plans
- Medical evidence supports zero carb diets for blood sugar stabilization and diabetes management when properly implemented
Understanding Zero Carb vs. Low Carb: The Critical Difference
Before diving into our comprehensive food list, it’s essential to understand the difference between zero carb foods and low-carb options. True zero carb foods contain absolutely no digestible carbohydrates, while low-carb foods may contain 1-5 grams per serving.
According to Harvard Health, this distinction matters significantly for individuals managing diabetes or following therapeutic ketogenic diets where even trace carbohydrates can impact blood glucose levels.
Zero Carb Food Classification System
True Zero
(0g carbs)
Animal Foods
Virtually Zero
(<1g carbs)
Select Plants
Low Carb
(1-5g carbs)
Limited Options
Zero Carb Animal-Based Foods: The Foundation
Animal-based foods form the cornerstone of any zero carb diet. Research from the University of Michigan confirms that unprocessed meats, fish, and eggs contain zero digestible carbohydrates, making them ideal for blood sugar control foods.
Beef and Red Meats (0g carbs per 3oz serving)
Poultry Options (0g carbs per 3oz serving)
Fish and Seafood (0g carbs per 3oz serving)
Shellfish and Crustaceans (0g carbs per 3oz serving)
Organ Meats and Specialty Items
Zero Carb Dairy & Eggs: What's Truly Carb-Free?
While most dairy products contain some lactose (milk sugar), several options qualify as zero or virtually zero carb foods for diabetes management. UC Davis research confirms these dairy choices are safe for strict carbohydrate restriction.
True Zero Carb Dairy (0g carbs)
Virtually Zero Carb Cheese (<1g per oz)
 Dairy Warning
Dairy Warning
Processed cheese products, cheese spreads, and “light” cheeses often contain added starches and sugars. Always check nutrition labels, as some varieties can contain 2-3g carbs per serving. Stick to aged, natural cheeses for the lowest carb counts.
The Best Zero Carb Processed Meats and Snacks
Processed meats can be tricky territory for zero carb snacks. While some qualify as truly carb-free, others hide sugars and starches. The CDC reports that over 80% of commercial processed meats contain added carbohydrates.
Safe Zero Carb Processed Options
 Hidden Carb Alert
Hidden Carb Alert
Avoid processed meats with honey, brown sugar, maple flavoring, or BBQ seasonings. These often contain 3-5g carbs per serving. Look for products specifically labeled “sugar-free” or “no carbs added” and always read ingredient lists for maltodextrin, dextrose, and corn syrup.
Zero Carb Fats and Oils: Pure Energy Sources
Pure fats and oils contain zero carbohydrates and are essential for satiety on zero carb diets. These high protein zero carb supporting fats help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Animal-Based Fats (0g carbs per tablespoon)
Plant-Based Oils (0g carbs per tablespoon)
Virtually Zero Carb Vegetables and Herbs
While no plant foods are truly zero carb, certain vegetables and herbs contain such minimal carbohydrates that they’re considered “free foods” by diabetes educators. These best zero carb vegetables provide essential nutrients while maintaining blood sugar stability.
Leafy Greens (<0.5g carbs per cup)
Fresh Herbs (<0.1g carbs per tablespoon)
Zero Carb Drinks and Beverages
Staying hydrated on a zero carb diet requires careful beverage selection. These zero carb drinks support your dietary goals while providing variety and satisfaction.
Always Safe Beverages (0g carbs)
Alcoholic Beverages (0g carbs)
 Beverage Caution
Beverage Caution
Diet sodas and sugar-free drinks often contain artificial sweeteners that may affect blood sugar in sensitive individuals. Flavored seltzers, flavored spirits, and mixers frequently contain hidden carbohydrates. Always check labels and stick to plain versions when possible.
Zero Carb Condiments and Seasonings
Proper seasoning makes zero carb eating enjoyable and sustainable. These condiments and seasonings contain no carbohydrates while adding flavor and variety to your meals.
Safe Seasonings and Spices (0g carbs per teaspoon)
Zero Carb Condiments
Zero Carb Meal Planning & Sample Days
Successful zero carb eating requires strategic meal planning to ensure nutritional adequacy and variety. This comprehensive meal planning guide provides practical templates and sample menus to help you implement zero carb foods for diabetes management effectively.
7-Day Zero Carb Meal Plan
Day 1: Foundation Day
- Breakfast: 3 scrambled eggs cooked in butter, 2 strips uncured bacon
- Lunch: 6oz grilled salmon with herb seasoning, side of spinach sautéed in olive oil
- Dinner: 8oz ribeye steak, small mixed green salad with vinegar dressing
- Snacks: Hard-boiled eggs, aged cheddar cheese cubes
Day 2: Variety Focus
- Breakfast: Cheese omelet with herbs, turkey sausage (sugar-free)
- Lunch: Tuna salad (mayo, no additives) over arugula
- Dinner: Pork chops with rosemary, steamed broccoli
- Snacks: Pork rinds, deli turkey rolls
Day 3-7: Rotation Pattern
Continue rotating proteins (chicken, fish, beef, pork) with different cooking methods and zero carb vegetable sides. Focus on variety in seasonings and preparation styles to maintain interest.
Portion Size Guidelines
Proteins: 4-8oz per meal (palm-sized portions)
Fats: 1-2 tablespoons added fats per meal
Vegetables: 1-2 cups leafy greens or ½ cup other low-carb options
Zero Carb Shopping List Template
Weekly Proteins
- 2-3 different cuts of beef
- 2-3 types of fish/seafood
- Chicken (various cuts)
- Eggs (2-3 dozen)
- Sugar-free deli meats
Fats & Dairy
- Butter, ghee
- Heavy cream
- Aged cheeses (3-4 varieties)
- Olive oil, avocado oil
- Animal fats (optional)
Zero Carb Extras
- Fresh herbs and spices
- Leafy greens
- Vinegars
- Mustard, hot sauce
- Mineral water, tea
Zero Carb Cooking Methods & Techniques
Mastering proper cooking techniques is essential for maintaining the nutritional integrity of zero carb food options while maximizing flavor and satisfaction. The right cooking methods can enhance nutrient bioavailability and create variety without adding hidden carbohydrates.
Optimal Cooking Methods for Zero Carb Foods
Grilling & Broiling
- Best for: Steaks, fish, chicken, vegetables
- Benefits: Enhances natural flavors, creates appealing texture, allows fat draining
- Pro tip: Use herb rubs instead of sugar-based marinades
Sautéing & Pan-Frying
- Best for: Eggs, leafy greens, thin cuts of meat
- Benefits: Quick cooking preserves nutrients, allows for flavor building
- Pro tip: Use animal fats or olive oil for best flavor
Slow Cooking & Braising
- Best for: Tough cuts of meat, organ meats
- Benefits: Breaks down connective tissue, concentrates flavors
- Pro tip: Skip flour thickeners, use reduction methods instead
Zero Carb Seasoning Combinations
Mediterranean Blend
Oregano, basil, thyme, garlic powder, sea salt
Smoky BBQ (Sugar-Free)
Paprika, cumin, black pepper, cayenne, salt
Herb de Provence
Rosemary, thyme, sage, marjoram, lavender
Blood Sugar Impact Analysis
Understanding how zero carb foods affect blood glucose levels is crucial for effective diabetes management and metabolic health optimization. Clinical research demonstrates significant differences in glycemic response between zero carb and traditional diets.
Clinical Blood Sugar Response Data
Zero Carb Meal Response
- 0-30 minutes: Minimal glucose change (<5 mg/dL)
- 30-60 minutes: Stable levels maintained
- 1-2 hours: Slight protein-induced gluconeogenesis
- 2-4 hours: Return to baseline without spikes
Mixed Carb Meal Response
- 0-30 minutes: Rapid glucose rise (40-80 mg/dL)
- 30-60 minutes: Peak glucose levels reached
- 1-2 hours: Insulin response causes rapid drop
- 2-4 hours: Potential hypoglycemic rebound
Long-Term Metabolic Benefits
Week 1-2: Initial Adaptation
- Reduced post-meal glucose spikes
- Decreased insulin requirements
- Initial weight loss (water and glycogen)
Week 3-8: Metabolic Shift
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Enhanced fat oxidation
- Stabilized hunger patterns
Month 3+: Long-Term Adaptation
- Reduced HbA1c levels (0.5-2% improvement)
- Improved lipid profiles
- Enhanced cognitive function
Interactive Zero Carb Food Tools
Rather than overwhelming you with a massive list of 200+ individual food items that would take considerable time to read through, we’ve created interactive tools that allow you to quickly find exactly what you need. These smart filtering and search systems help you discover zero carb food options efficiently based on your specific requirements.
Portion Size Calculator
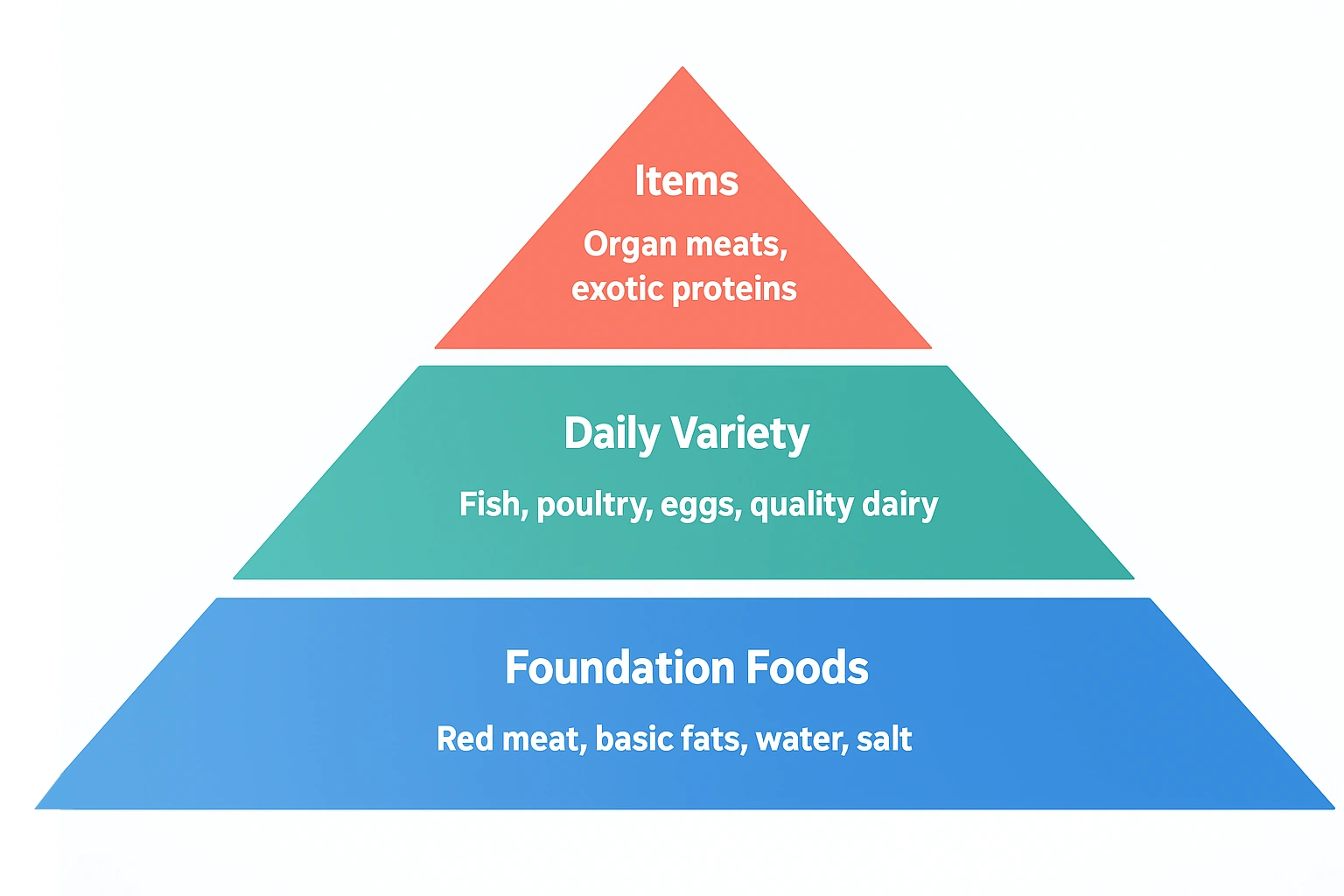
Advanced Zero Carb Diagrams
Zero Carb Food Pyramid
Daily Meal Timing Optimization
6:00 AM
First Meal
High protein, moderate fat
Example: Eggs + bacon
12:00 PM
Midday Meal
Balanced protein + vegetables
Example: Salmon + spinach
6:00 PM
Evening Meal
Higher fat, quality protein
Example: Ribeye + salad
Nutrient Density Comparison
Daily Meal Timing Optimization
Disclaimer:
The information provided on MD-Pilot is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recomended Articles
View AllWeekly Health Intel
Get evidence-based health tips, latest research, and exclusive guides delivered weekly




